CHARTERED ACCOUNTANCY PROFESSION IN THE DIGITAL ERA
A day in the life of a Chartered Accountant
When was the last time you and your team members left office on time on a workday during a tax season? Sounds like a seemingly impossible task?
This is probably because much of the day-to-day activities of Chartered Accountants include manual, repetitive tasks such as data entry, data verification, tax calculations, reconciliations, and report generation. In traditional Chartered Accountancy practices, a significant part of the work is performed outside of client’s ERP systems and as much as 60% of the activities are still being done manually on spreadsheets. To begin with, they find, extract, and manipulate relevant data into a usable format. This data is then moved in and out of spreadsheets to complete a variety of necessary calculations and computations. Additionally, handling these tasks manually leads to delays in transaction processing and reporting, continuous errors and misstatements, and difficulty in storing large data on papers.
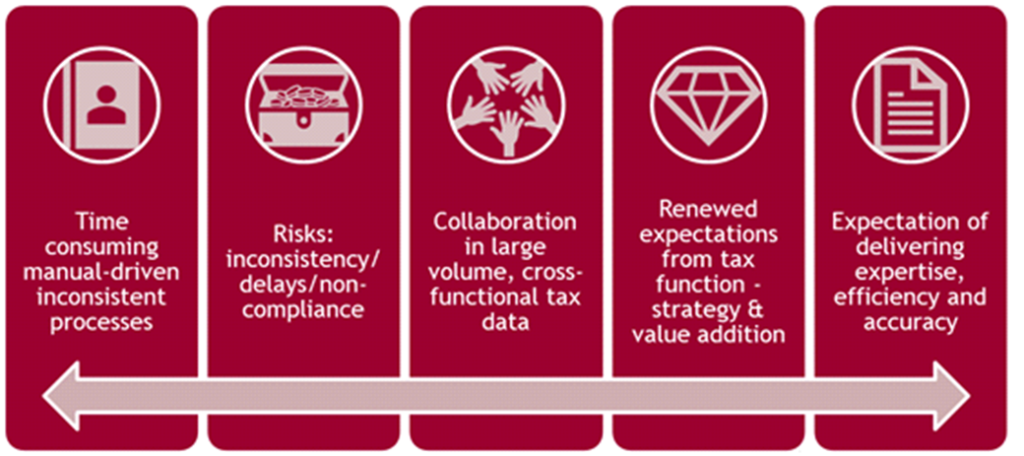
However, traditional practices need to be modernized. In past few years, challenges in form of new GST regime, cryptocurrency, blockchain, etc. have made it imperative to expand skillsets beyond the traditional practise for managing tax compliance, audit, litigations, due diligence, etc. Hours of manual labour are not the best use of the knowledge and expertise of Chartered Accountants as their time comes at a high cost to the businesses they serve. To maximize the value of a Chartered Accountants, more effective solution would be to use their skills and knowledge to identify tax opportunities, manage risks, and work with client to optimize value of client’s business.
Why is there a push towards Tax Automation?
Chartered Accountants are the economic ambassador between people & businesses who play different roles in the global economy such as an Accountant, Financial Planner, Tax Consultant, Auditor, Compliance & Litigation Manager, Management Consultant, etc. Further, due to increase in the Indian & global tax compliance and reporting requirements, corporates are now moving more towards outsourcing accounting & tax compliance work as it can be a cost-effective way to manage their tax affairs, which means more work opportunities for practising Chartered Accountants. With new regulations coming to force and emerging opportunities, new responsibilities assumed by Chartered Accountants have evolved their role as indispensable partners in business progression. A wrong decision can have a significant and lasting impact on the business. Thus, it is important that they streamline and strategically manage all tax activities with a focus on managing risks without any potential snags. The conventional way of managing compliances, litigations, calculations, reconciliations, litigations, etc. would need transformation to meet with the demands of the current environment and achieve the below.
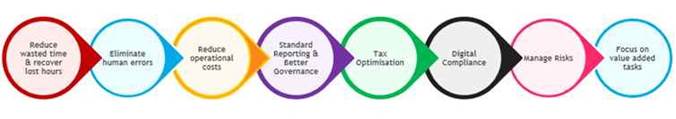
In the recent years, the Chartered Accountancy profession has already experienced significant technological shift due to transition from the indirect tax regime to GST, e-filing returns, online registrations, e-assessment, etc. This has specifically led businesses and their consultants to adopt a well- built technological infrastructure to help businesses remain tax compliant. Further, to keep up with rate of adoption of technology by tax authorities, there is now a pressure on Chartered Accountants who serve businesses to make a shift from people driven to process driven practices. However, this shift could be overwhelming, but could be made simple if broken down into phases so that it’s not quite so daunting. A good understanding and analysis of the nitty-gritties of technology & automation, would make this shift easier to navigate. Let’s broadly understand a few technology trends to keep up with and its application in day-to-day work:
- Cloud Based Software: Use of cloud-based system is the delivery of hosted services via the internet. The main benefits of using cloud-based software is the flexibility, performance and security that they provide. Use of cloud-based software tools like tax return filing tool, tax management tool, litigation management tool can aid in automating complex calculations, computations and handle compliances and reporting of data for tax purposes at relatively low cost. Additionally, it allows documents and information to be digitized on a centralised location and shared across multiple computers and devices, allowing Chartered Accountants to collaborate and share work within teams and their clients.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA is a software that can be programmed or instructed by end users to perform repetitive, high-volume tasks. The rules-based tasks like automated extraction of data from government portals and tracking important events, automated data entry, filing returns, etc. Automated data entry means consistent and reliable data can be imported at a faster pace into reports which increase efficiency and accuracy. Multiple bots undertaking different tasks at a time can be built forming a virtual workforce. Implementing robotic processes could get repetitive compliance work out of the way so that practitioners can focus on doing what they are trained to do, i.e., strategize reduction in assessment, identify tax issues, and implement sustainable solutions.
- Optical Character Recognition: The ability to scan documents like invoices, tax notices, bank statements, returns, challans, etc. increases operational efficiency and reduce re-entering data for carrying out multiple operations. OCR technology reads the machine-readable files to match images with recognized text characters to transmit data accurately. This increases file searchability through indexing and extraction of key data points which can also help in automating data entry. This technology can help digitise the data in documents, statements, orders, etc.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is a broad term consisting of variety of components. Equipping computer systems with something akin to human intelligence. AI based tools can be usedfor classifying large volume of unstructured data into logical taxonomies, identifying potential tax frauds, predicting outcome of an ongoing litigation, and providing data-driven suggestions/ recommendations. Activities like sensing, thinking, acting can be facilitated through AI based tools which can help in identifying possible tax deductions, tax credits and key areas for possible tax savings, and also to compare pricing structures to ensure fairness of transfer pricing in global transactions.
- Natural language processing (NLP): NLP which refers to the ability of the computer to recognise & understand human speech can be used to convert scanned images. The machine vision ability of AI can be used to recognise the patterns and understand the text and extract only relevant information from scanned documents. This ability to scan documents like invoices, tax notices, returns, bank statements, returns, challans, etc. increases operational efficiency and reduce re-entering data. The Optical Character Recognition technology utilizes Natural Language Processing for machine-readable files to match images with recognized text characters to transmit data accurately. This increases file searchability through indexing and extraction of key data points which can also help in automating data entry.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML can be used to analyse and classify data through logical reasoning, algorithms, and mimicking human cognitive processes. Relying entirely on data, machine learning involves constructing computer algorithms that automatically improve themselves by finding patterns in existing data without explicit human intervention. These algorithms also allow input of new data and help in analysing huge amount of data with various combinations. As the legal domain produces huge amount of information, intelligent techniques are required to provide a better grouping, tidying up, organise and analyse the legal documents which could be structured, semi-structured or unstructured. Complicated tasks like forecasting, predicting outcome based on trends in historic data (e.g., transaction account classification, predictive models for forecasting & planning), conducting risk assessments, formulating risk management strategies (e.g., determination of tax impact/implications of a transaction), analysing customer behaviour, running complex reconciliations (e.g.,26AS reconciliation, GST reconciliation, etc.) can be easily undertaken using sophisticated and statistical machine learning principles.
- Deep Learning (DL):DL more closely mimics human learning through the use of artificial neural networks to perform more complex tasks such as visual object recognition and providing suggestive answers to users based on intent of the query. Features like chat bots use DL to respond to tax queries on real-time basis based on pre-defined & curated knowledge base.
- Blockchain: Blockchain has the potential to decentralize information, which is real-time and cannot be altered, which means the information is completely transparent. Blockchain is already being utilised by the legal industry, to automate execution of an agreement so that all participants can be immediately certain of the outcome. It is crucial to evaluate how Blockchain can be implemented to create a single source of truth to consume financial and tax data.
Embracing Digital Transformation
Embracing digital transformation will enable Chartered Accountants and their clients’ businesses to modernize legacy processes, accelerate efficient workflows, get deeper insights into trends, risks, potential opportunities and manage the bottom line. However, these insights cannot be obtained without data. The peculiar properties of data and its ability to produce deep insights makes it not merely a new asset, but an asset that businesses need if they want to thrive in today’s digital era.
As nearly 70-75% of data used for managing client’s tax compliances comes from common data sources like ERP of the client, government portals and third-party sources, creating a centralized data warehouse opens many opportunities to increase the efficiency of automation & technologies built on top of this data. It can generate solutions to complex business problems and add value to clients’ businesses through data analytics, visualization tools, optimization methods, machine learning, and predictive analysis. Creating a single source truth in form of a centralized data warehouse is vital to ensure everyone within client’s organisation and the Chartered Accountants base their business decisions on the same data. Further, when you have thousands of documents and a voluminous financial & tax data to analyze, data analytics can help gain insights, understand relationships and trends across data to often find things you didn’t know would be in there.
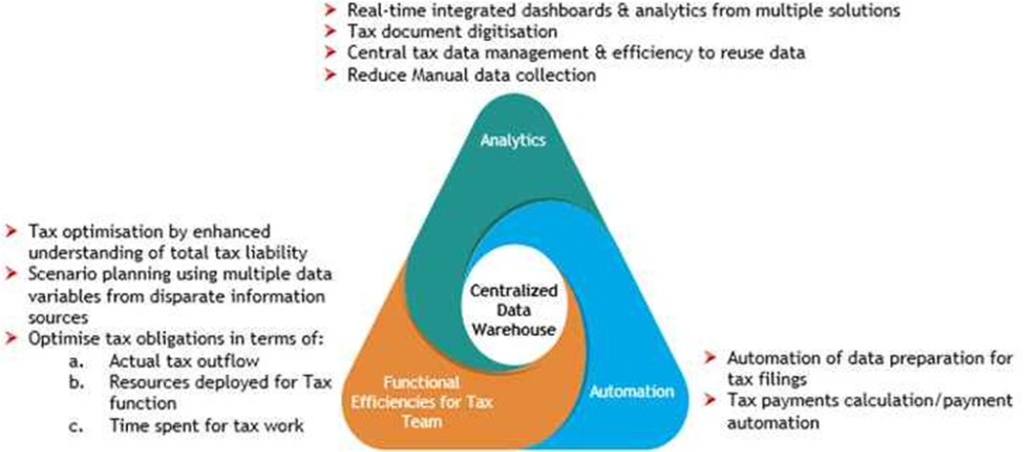
Well-integrated cloud-based solutions built on top of such centralized data warehouse can transform the way businesses have been operating at local as well as global level and deliver the following:
- Project & Document Management:
- Streamlining work processes and documents right from inception of a project to its conclusion
- Ability to track and monitor information and eliminate project risks
- Well-indexed documents providing real-time access to authorised users to data and information anytime from anywhere
- Increased collaboration within team members and with clients
- De-risking loss of data & information due to change of team/ consultants
- Tax calculations, computations & reconciliations:
- Automated sourcing, validation & processing of data from common data warehouse required for classifying transactions, tax determination, performing reconciliations, etc.
- In-built logics for computing taxable income, deductions, and calculation of total tax liability
- Filing of returns and reports required under tax legislations
- Building automated reconciliations based on complex logics viz. 26AS Reconciliation, GST Reconciliations
- Compliance &Risk Management:
- Tracking statutory due dates
- Tracking compliances and instances of non-compliances
- Highlighting impact on non-compliances in form of interest, penalty, etc.
- Working Capital Management:
- Tracking status of tax demands and refunds
- Tracking unutilized tax credits
- Tracking eligible losses available for set-off in subsequent years
- Highlighting impact of events which could lead to blockage of working capital
- Tax Certification & assurance:
- Ease of auditing, validating data & documents required for generating certificates
- Robust approval process, ensuring reduced turnaround time and timely issuance of certificates
- Transparent end-to-end certification process
- Litigation Management and Tax Provisioning:
- Tracking notices, responses to notices and submissions made to tax authorities
- Tracking important events like upcoming hearing date, submission date, time barring due dates, etc.
- Tracking journey and outcome of cases, issues, and grounds across multiple appeals
- Evaluating probability of outcome basis historic litigation data
- Ability to tracking contingent liability & calculate actual tax liability
- Automated calculation of interest cost on contingent liability
- Knowledge &Research Management:
- Improving productivity by leveraging existing knowledge to reduce risk and turnaround time
- Institutionalisation of research and knowledge for improved decision making and strategic planning
- Reduced cost of employee training
- Faster development of new technical approaches
- Tracking management information & reporting:
- Interactive dashboards and reports providing insights into tax data
- Tracking status of compliances, ageing and impact of overdue non compliances, period-wise tax payments, etc.
- Tracking of important events and action points for formulating tax and risk management strategies
- Formulate important KPIs for business based on intelligent data analytics
Impact of going Digital
The progression in technology field and the use of technology in day-to-day work life invites a call to action for Chartered Accountants to adapt quickly through regular training programs and make the most of upcoming opportunities to stay relevant & better their own business and match clients’ expectations.
Let’s take a few examples of current tax processes where automating manual processes have magnified the efficiencies of Chartered Accountants and helped in delivering value to clients
- Managing compliances for dividend pay-outs for a large number of resident and non-resident shareholders
| Approach of a traditional practitioner (People driven practice) | Approach of a tech savvy practitioner (Process driven practice) |
| Physical document management for resident & non- resident shareholders | Complete digitisation and repository of documents for resident & non-resident shareholders |
| Time consuming process of data compilation and verification | Smart data capture, indexed document upload, inbuilt validations help quicken the whole process |
| Manual calculation of TDS to be deducted on each remittance | Automated tracking of thresholds and determination of tax to be deducted on each remittance |
| Maintenance of multiple spreadsheets, files resulting in duplication and chances of error | Relational data structure to avoid duplication and mitigate errors/omissions |
| Manual and spreadsheet assistance to track the remittances made | Dynamic dashboards and reports to facilitate efficient tracking |
| Lack of transparency to the client – to understand the stage at which Form 15CB is pending for proposed remittances to non-resident shareholders | Complete transparency – client can log-in to the portal and check the stage at which Form 15CB is pending |
- Managing reconciliation of TDS/TCS Credits in books with TDS/ TCS credits appearing in Form 26AS and tracking action points
| Approach of a traditional practitioner (People driven practice) | Approach of a tech savvy practitioner (Process driven practice) |
| Manual exercise of calculating eligible TDS/ TCS | Automated reconciliation with no manual |
| Inefficient manual processes are prone to errors which are difficult to track and amend | Technology driven process providing accuracy and easy tracking of action points |
| Difficulty in manually tracking of brought forward unutilised credits, utilisation of such credits in current year and carry forward of unutilised credits to subsequent years | Dynamic Dashboards & reports for tracking customer wise reconciliation status, status of utilisation and unutilised credits across multiple years |
| Delay in manual follow up with customers/ vendors for may impact cashflow and tax | Automated emails to customers/ vendors for seeking clarifications & tracking responses on such issues help in decision making |
| Inability in reconciling balances as per books vs Form 26AS leading to blockage of working capital | Effective working capital management through efficient reconciliation process |
| Hidden cost involved in searching of documents during assessment proceedings | Mitigation of hidden cost & Assessment ready – Availability of necessary documentation/ reports at |
| Challenges in work continuity due to inefficient transition of data & documents to new team members or consultants | Undisturbed transition of documents & information to new team members or consultants due to easy retrieval of data & information as all the necessary data is stored on centralised location |
- Managing compliances under GST regime
| Approach of a traditional practitioner (People driven practice) | Approach of a tech savvy practitioner (Process driven practice) |
| Manual handling of massive data through multiple spreadsheets linked to each other | Ability to handle, validate and process large volume of data through technology |
| Repetitive manual processes which are prone to error | Automation of repetitive tasks providing higher accuracy |
| Lack of insights and trends into data and processes | Dynamic and interactive dashboards providing intelligent insights into data & processes |
| Performing manual reconciliations within multiple datasets which is time consuming with uncertainty of accuracy of output | Automated & Real time analysis of potential mismatches, data reconciliation issues within multiple datasets under different provisions of indirect as well as direct tax (clause 44 of Tax Audit) |
| Difficulty in tracking changes in law and manually analysing changes & implementing the same in current manual processes | Auto updates in technology on account of changes in law providing seamless experience in handling compliances |
| Handling pre-compliance, compliance and post compliance activities manually leading to wastage of time which could have been otherwise spent on value adding activities for increasing value of business | Automation of invoice generation according to government specified schema, seamless integration of all processes to manage compliances, automated periodic reconciliations |
| Difficulty in managing workflows, manual tracking of due dates, status of compliances | Regular reminders, notifications of important events or due dates, accurate tracking of status of compliances assisting in managing risks and managing workflows through technology |
| Challenges in work continuity due to inefficient transition of data & documents to new team members or consultants | Undisturbed transition of documents & information to new team members or consultants due to easy retrieval of data & information as all the necessary data is stored on centralised location |
- Managing compliances under the evolving Customs environment
| Approach of a traditional practitioner (People driven practice) | Approach of a tech savvy practitioner (Process driven practice) |
| Physical storage of documents creating difficulty in retrieving and accessing information and leading to misplacement/ loss of documents | Ability to store the data/information in a logical, intelligent, analytical, and searchable structure, enabling businesses to track their transactions smoothly |
| Manual extraction of data points from Shipping Bills and Bill of Entries and tracking information through spreadsheets | Substantial reduction of manual effort required in recording, analysing, maintaining and retrieval of Shipping Bills, Bill of Entries and Export Promotion scheme Automated extraction of information using technologies like Optical/Intelligent Character Recognition, Machine Learning, Cognitive Services |
| Manual tracking of status of refunds/ incentives/ obligations/ compliance status | Real time tracking of refunds / incentives, status of pending obligations and compliance status |
| Lack of control over processes, compliances and increased operational cost | High Governance, cost optimisation, incentive management, obligation management, customs duty calculator, obligation pendency calculations |
| Lack of insights and trends into data and processes | Dynamic and interactive dashboards providing intelligent insights into data and processes |
| Challenges in work continuity due to inefficient transition of data & documents to new team members or consultants | Undisturbed transition of documents & information to new team members or consultants due to easy retrieval of data & information as all the necessary data is stored on centralised location |
The above examples clearly highlight the benefits of using technology to undertake complex tasks with more control over data, people, and processes. Chartered Accountants and their staff have been fearing that automation has the potential to eliminate jobs, however, the reality is that businesses need transformation in form of automation to stay competitive and make their staff more efficient and satisfied. Technology literacy and the benefits of harnessing different forms of technology for better use of data and optimizing resources is pivotal to any tax practitioners’ success to equip themselves and lay the foundation for a brighter tomorrow.
