TAXISSUESFOR DUAL TAX RESIDENT INDIVIDUALS
Albert Einstein once said “The Hardest thing in the World is to understand the income tax”
Imagine the magnification of complexities if an individual becomes tax resident of two countries. Dual tax residency leads to tax compliances in two geographies and going through mazes of tax treaty between countries as well as domestic tax laws of both jurisdictions. We will be looking ahead today on step-by-step tax solution for issues from Indian tax perspective.
Step 1 : Ascertaining Residential Status of Individual
- Person need to ascertain whether it is a Resident or Resident but not ordinarily resident in India
- For claiming any Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) benefit, Individual need to identify himself as tax resident of either country
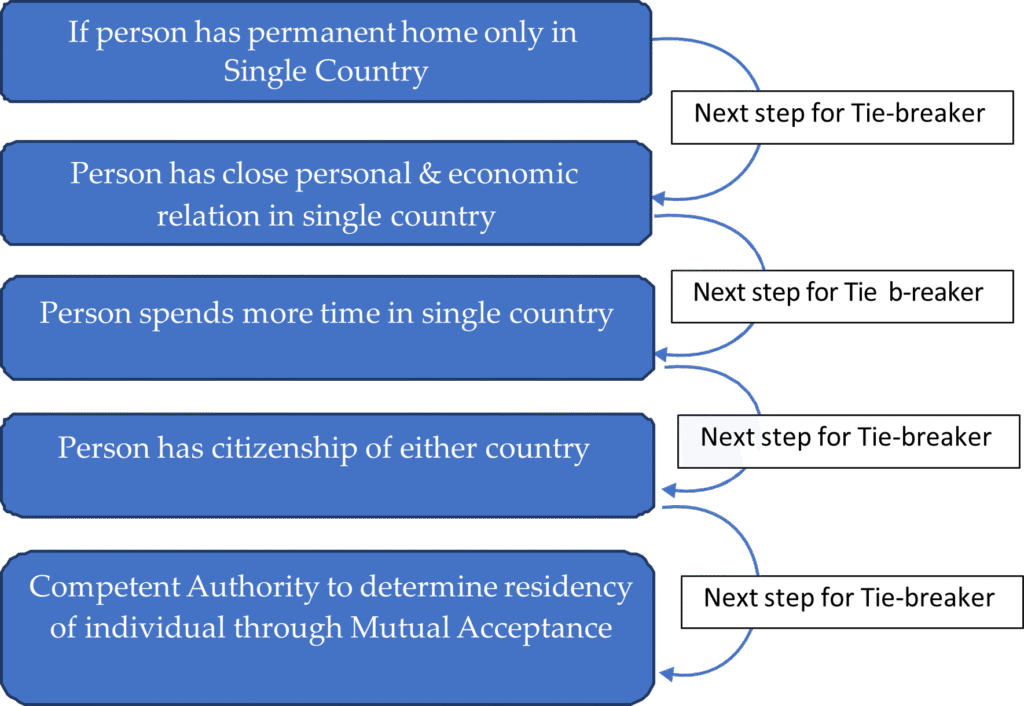
Determining tax residency under DTAA
Generally, tax treaties provide provisions to determine residency of individual in cases of individual being resident of both countries.
Summarisation of process to determine Individuals residency as per Article 4: Resident from OECD Model tax convention of 2017 is as follows:
Step 2 : Computation of Income
As per section 90 & 90A of income tax act, assessee may select provisions of income tax act or DTAA whichever are more beneficial. While computation of Income as per Income tax, taxability of income from various sources needs to be determined along with provisions of DTAA.
Discussing major source of income for individuals and tax considerations to be taken by Individual:
| Source of Income | Model DTAA taxability | Taxability in Foreign Jurisdiction as per OECD model tax convention* | Taxability in India | |
| Resident | Resident but not ordinarily resident | |||
| Income from Salary | Salary income earned by employment in foreign country will be taxed in that foreign country if conditions laid down in treaty are achieved. Generally, DTAA provides for following 3 conditions: | Individual need to assess taxability as per DTAA | Taxable in India | Not Taxable in India if taxed abroad. |
| 1. Stay of individual exceeds number of days specified as per specific DTAA | ||||
| 2. Remuneration is paid by or borne by resident of foreign country | ||||
| 3. Remuneration is borne by Permanent establishment in foreign country | ||||
| Income from Immovable Property | If DTAA contains Article of Immovable property: 1. Income earned from immovable property situated in foreign country will be taxed in country where it belongs. | Taxable in foreign country | Income will be Taxable in India | Not taxable in India |
| 2. Home country may tax such income | ||||
| Source of Income | Model DTAA taxability | Taxability in Foreign Jurisdiction as per OECD model tax convention* | Taxability in India | |
| Resident | Resident but not ordinarily resident | |||
| Income from Capital Gains | Capital gains income earned by sale of immovable property or movable property situated in foreign country will be taxed in country where it belongs. | Taxable in foreign country | Income will be Taxable in India | Not taxable in India |
| However, home country may as well tax such income. | ||||
| Independent Personal Services (Professional Services) | Income from Professional services earned from foreign country is taxable in country of residence. Such income will be taxed in foreign country as well if that income is earned through fixed base in foreign country or stay in foreign country exceeds number of days defined. | Individual need to assess taxability as per DTAA | Taxable in India | Not Taxable in India if taxed abroad. |
Step 3 : Claiming relief of foreign tax credit
For claiming credit of foreign tax credit, Individual need to determine relief as per DTAA. For providing further clarity on mechanism to claim such relief, CBDT had issued Foreign Tax Credit Rules.
Resident Individual can claim deduction of foreign taxes paid. However, relief in India can be claimed with riders and conditions attached to claiming foreign tax credit are as follows:
- Credit shall be claimed in year in which income is offered to tax in India. In case of income offered across multiple years, credit of foreign tax can be claimed in the proportion to which income is offered to tax
- Foreign taxes credit shall not be disputed in overseas jurisdiction. Individual may claim credit in India within 6 months of settlement of dispute overseas.
- Individual shall not be claiming refund of such taxes in overseas jurisdiction
- Tax credit shall be available only to the extent of tax applicable as per DTAA between India and respective country
- Tax credit shall be lower of tax liability as per Income Tax Act and tax actually paid overseas.
